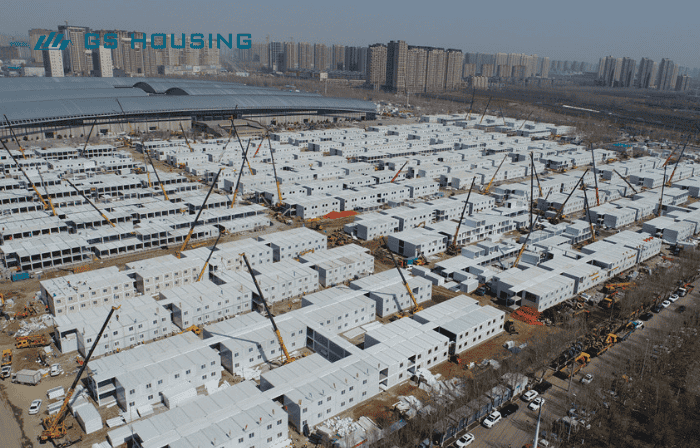
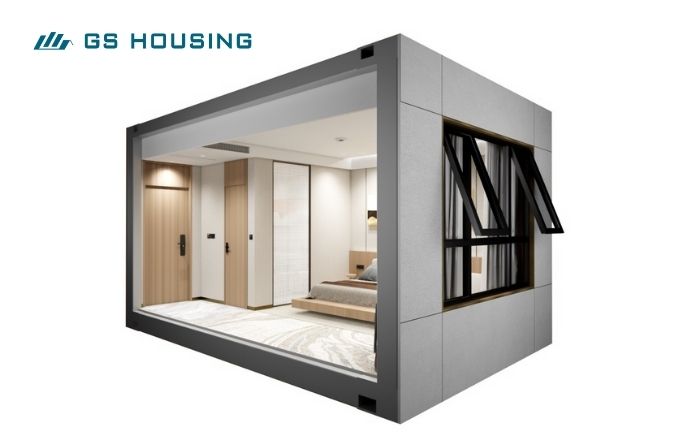
1. What is a Modular Hospital?
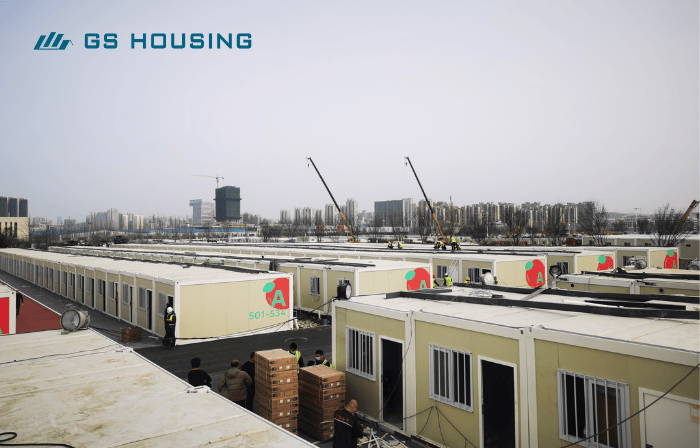
A modular medical facility is a new type of medical building model where hospitals are built “in a factory”.
Simply put, the various rooms of the hospital (wards, operating rooms, ICUs, etc.) are prefabricated in a factory, with wiring, water pipes, air conditioning, medical gas systems, and other equipment installed. These are then transported to the site and assembled into a fully functional hospital.
Features of Modular Hospitals:
* Factory Prefabrication: Manufactured in a controlled environment, ensuring the quality of the portable hospitals.
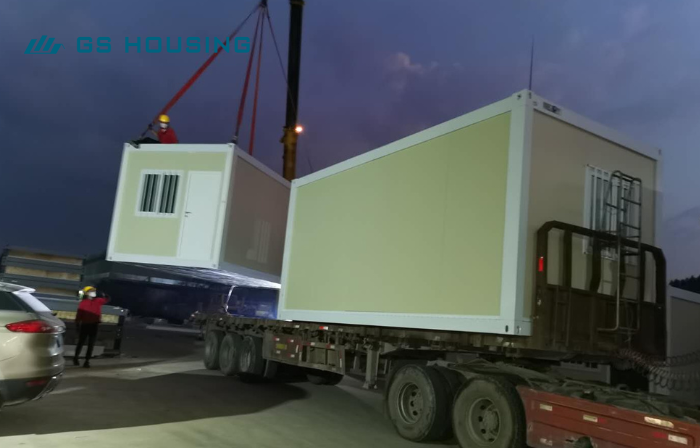
* On-site Assembly: Modules can be quickly assembled after arriving on-site.
* Multiple Forms: temporary hospitals, semi-permanent hospitals, or long-term multi-story container hospitals.
* Flexible Layout: Size can be freely combined according to needs.
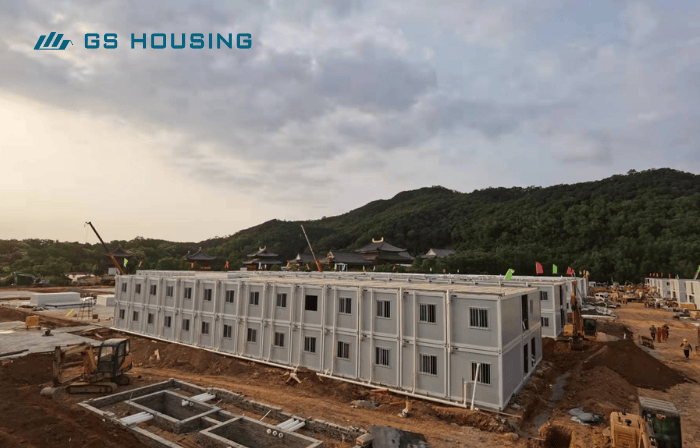 |
 |
Key Advantages of Modular Hospitals:
* Faster construction speed: the emergency container hospitals are more than 50% faster than traditional hospitals;;
* Standardized factory production, more stable quality;
* Reduced construction waste, more environmentally friendly;
* lower costs;
* Can be expanded or relocated at any time, flexible and convenient.
 |
 |
2. Modular Hospitals vs. Traditional Hospitals
| Aspect | Modular Hospital | Traditional Hospital |
| Construction Time | 50–70% faster, parallel production | Long on-site process |
| Quality Control | Factory-controlled precision | Variable site conditions |
| Flexibility | Easily expanded, relocated | Fixed structure |
| Environmental Impact | Lower waste and noise | High material consumption |
| Budget Predictability | Fixed cost manufacturing | Cost overruns common |
| Disruption | Minimal to surrounding areas | High disruption during build |
Prefabricated hospitals represent a faster, more flexible, and more environmentally friendly new model for medical construction.
 |
 |
3. Modular Hospital Types
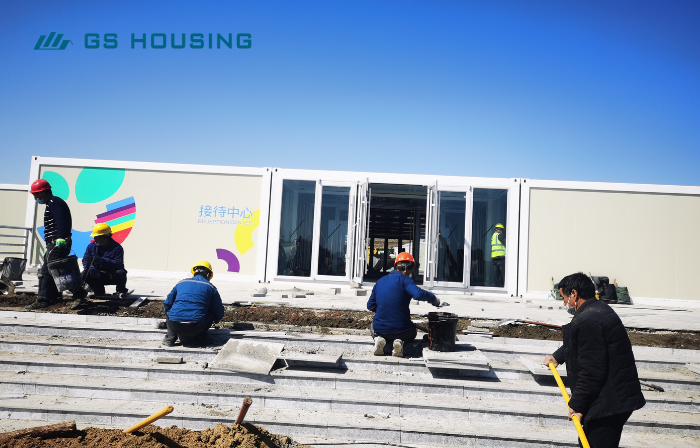
Emergency flat-pack hospital: These are facilities that can be set up quickly in case of a pandemic, disaster, or humanitarian crisis. Set up in two to four weeks.
Permanent Modular Hospitals: These are multi-storey buildings with all the medical facilities needed for long-term use. They last more than 50 years.
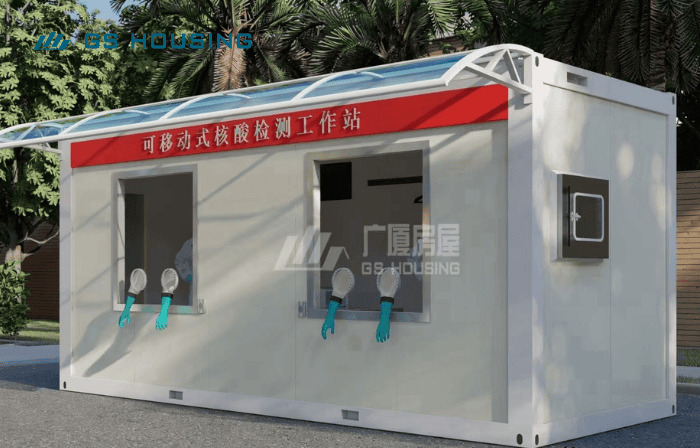
Mobile or Portable Hospitals: These are small units that can be mounted on trucks or trailers for short-term missions or field operations.
Rural Modular Clinic: these container clinics can provide health care to areas that don’t have enough of it.
Military Field Hospitals: Strong, weatherproof units made for defence and emergency use.
4. Design and Construction Technology of Modular Healthcare
Mobile Hospital Construction Process:
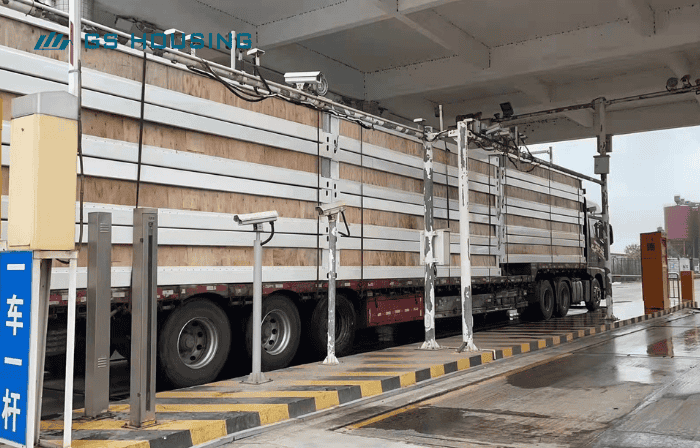
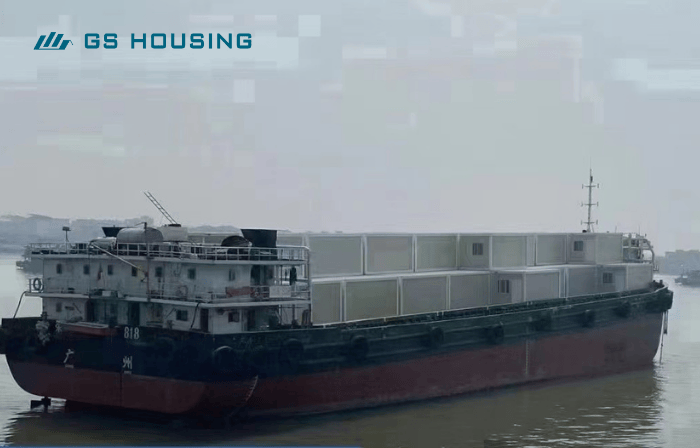
Confirm requirements—building design—production—transportation—installation—handover
Every step follows strict medical and construction rules set by ISO, WHO, and CE.
Compared to traditional methods, prefabricated medical buildings can save 40-60% of time, reduce on-site construction, and mitigate the impact of weather.
Materials and Technology
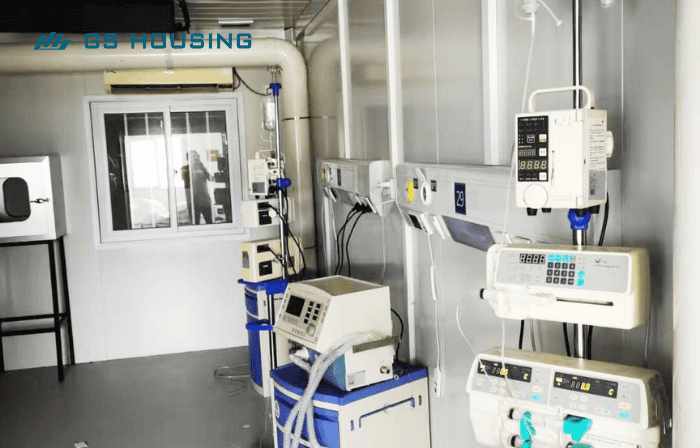
Container-based hospitals typically utilize steel structures, clean room wall panels, and composite insulation materials to ensure safety and hygiene.
Prefab medical facilities are equipped with smart sensors and IoT systems, have reserved solar energy interfaces, and integrate medical gas and vacuum systems.
These technologies make the portable hospital more energy-efficient, intelligent, and easy to maintain.
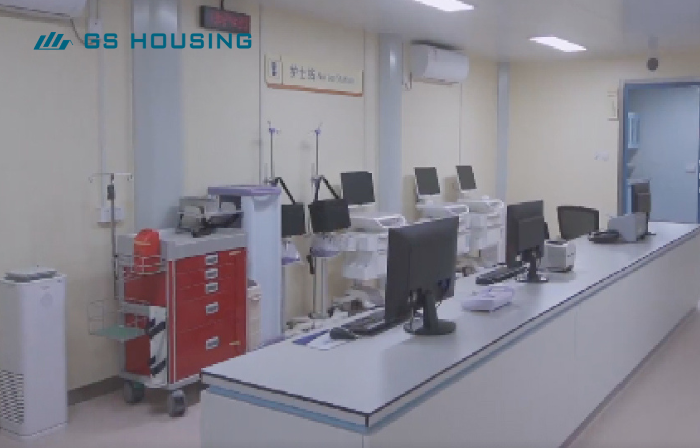
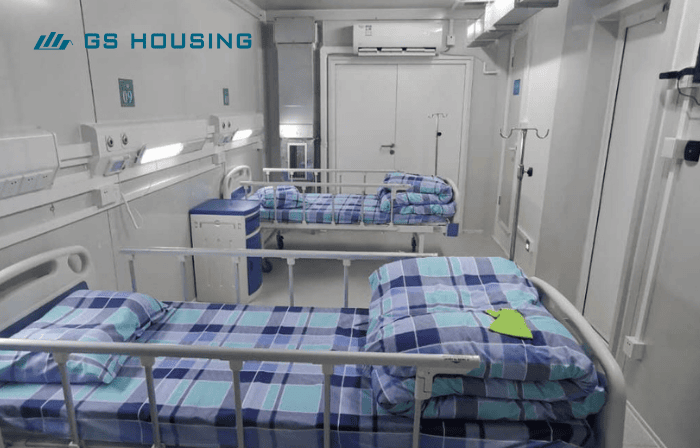
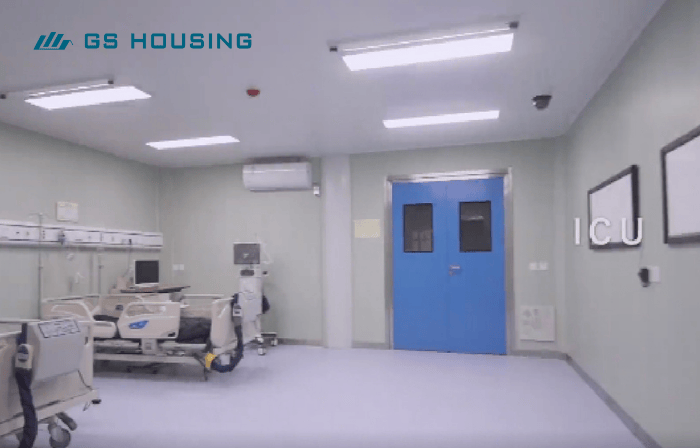
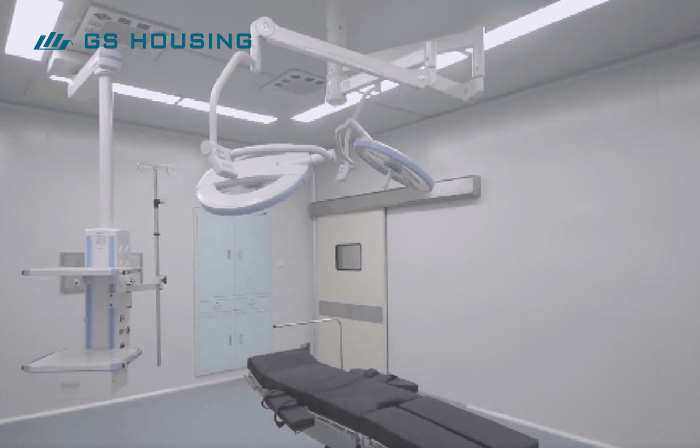
Intensive Care Unit and Operating Room Modules
Compliant with international clean room standards (ISO 14644); equipped with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to control air quality; integrates medical gas, power, and alarm systems; ready for immediate use after on-site installation.
Advantages: quick construction speed, stable environment, and rapid response to emergency expansion hospital needs.
Air Conditioning and Purification System (HVAC)
Mobile medical units use HEPA filters that can trap 99.97% of particles; create areas with different air pressures to stop infections from spreading; have automatic controls for temperature and humidity; and monitor conditions in real-time, all while saving a lot of energy.
This ensures clean, safe, and energy-efficient air within the emergency medical shelter.
 |
 |
 |
5. Global Application Cases
Emergency Hospitals
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital was a prime example of a modular hospital, built in just 10 days and boasting over 1,000 beds. Similar prefab hospitals have also been rapidly deployed in Africa and Europe.
Advantages: A fast-assembly hospital can be built within weeks, meeting large-scale medical needs during crises; it can be disassembled or relocated after the crisis.
Rural Modular Clinics
Serving areas with limited medical resources: low cost, quick installation; can utilize solar energy and self-circulating water systems; modular design facilitates expansion and upgrades; improves maternal and child health and emergency medical conditions.
Army Modular Hospitals
The mobile military hospital is rugged and durable, resistant to rain and wind, transportable by air, truck, or ship, and includes operating rooms, intensive care units, and pharmacies. It can be assembled within 48–72 hours.
Both military and humanitarian medical camps extensively utilize these modular hospitals.
 |
 |
 |
6. Economic and Business Insights of Modular Hospital Industry
Comparing the costs of modular hospitals and traditional hospitals
Cost savings of 20–30%.
Less time spent building means lower overhead costs.
Used materials more efficiently and cut down on waste.
Lower on-site supervision expenses.
For instance, a modular container hospital with 100 beds costs 25–30% less than a traditional hospital of the same size.
The benefits of modular hospitals in terms of ROI and lifecycle
Assets that can be used again: Modules that are moved or used for new projects.
Low Maintenance: Strong materials lower long-term costs.
Quick Return: An earlier start date means faster income.
Sustainable Investment: Green design saves money on energy.
High Resale Value: Modular assets keep their physical and financial value.
How quickly can a modular hospital be built?
A portable mobile hospital with 50–100 beds: 30–45 days
A detachable prefab hospital with 200 to 500 beds:60 to 90 days
Large permanent modular hospitals: 4–6 months
15. Benefits of Green Building and Sustainability
Benefits of Sustainability: 60% less waste of materials.
50% less energy is used during building.
Steel that can be recycled and modules that can be used again.
Shorter timelines mean fewer CO₂ emissions.
 |
 |
7. Global Standards for Modular Construction Hospitals
Modular hospitals must comply with global healthcare building standards:
ISO 9001/14001: Quality and Environmental Management;
ISO 14644: Cleanroom Standards;
NFPA 99/101: Medical and Fire Safety;
WHO, CE: International Healthcare System Compliance.
This ensures the prefab container hospital‘s safety, reliability, and international compatibility.
Rules for temporary and permanent modular hospitals
Temporary modular hospitals must follow emergency construction codes. The approval processes are expedited and simplified.
Permanent container hospitals must follow all codes for structure, fire safety, and access.
 |
 |
8. The Future of Modular Healthcare Building Trends
Digital Design Integration: Real-time collaboration leveraging artificial intelligence and Building Information Modeling (BIM).
Smart Hospital Systems: Energy and patient management through IoT;
Hybrid Buildings: Combining the advantages of traditional and modular construction;
3D Printing and Robotic Production: Higher automation;
Net-Zero Energy Design: Achieving net-zero emissions using renewable energy.
The modular hospital of the future will be a faster, smarter, and greener healthcare infrastructure.
 |
 |
9. How Modular Construction is Changing Healthcare Around the World
Impact on the world:
Makes it easier for people in developing countries to get health care.
Increases the ability to respond to emergencies.
Lessens the carbon footprint of medical infrastructure.
Allows urban healthcare systems to grow in a flexible way.
Conclusion:
Modularization is Reshaping the Global Healthcare System
Modular hospitals are not just a construction method but a revolution in global healthcare construction.
The modular house enables remote areas to access modern medical facilities, makes emergency response more efficient, and makes hospital construction greener, more flexible, and more economical.
From design and production to implementation, modular hospitals represent the future direction of healthcare—rapid construction, intelligent operation, and sustainable development.
Post time: 02-12-25







